Describe the Steps of the Cell Cycle
The Cell Cycle Phases view describes the cell cycle phases and checkpoints and includes illustrations of the cells chromosomes. Has provided students with a learning resource for cell biology microbiology immunology and microscopy through the use of mobile-friendly interactive animations video puzzles quizzes and study aids.
The Cell Cycle And Mitosis Review Article Khan Academy
The mitotic phase is the shortest part of the cell cycle.

. The OAA is converted to Malic Acid and then transported from the mesophyll cell into the bundle-sheath cell where OAA is broken down into PEP plus carbon dioxide. Basic Cell Parts Involved in Mitosis Cell membrane. Students can toggle between two different views of the cell cycle by pressing the text in the center of the graphic.
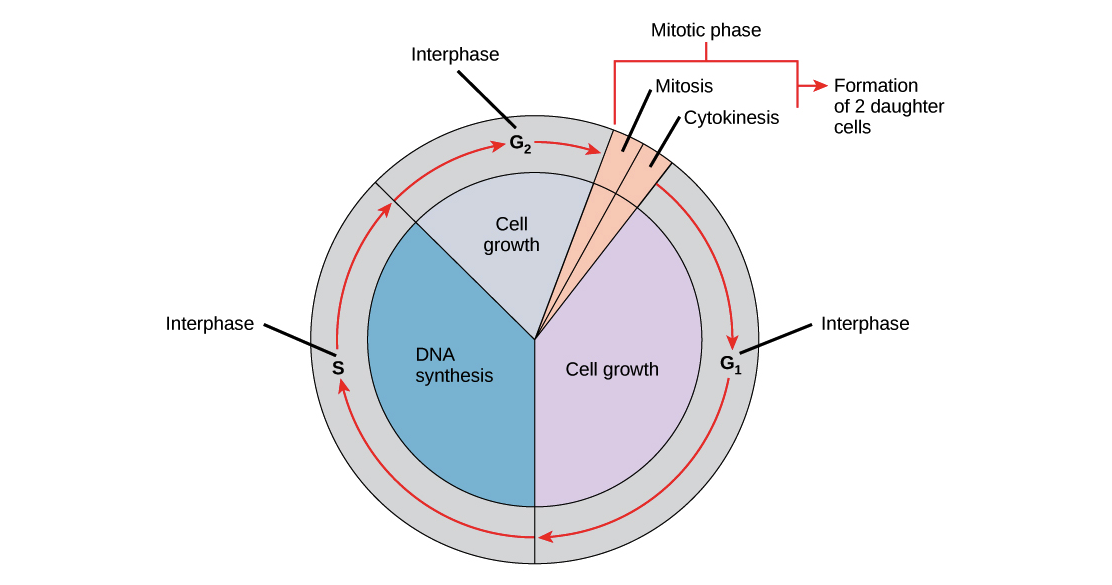
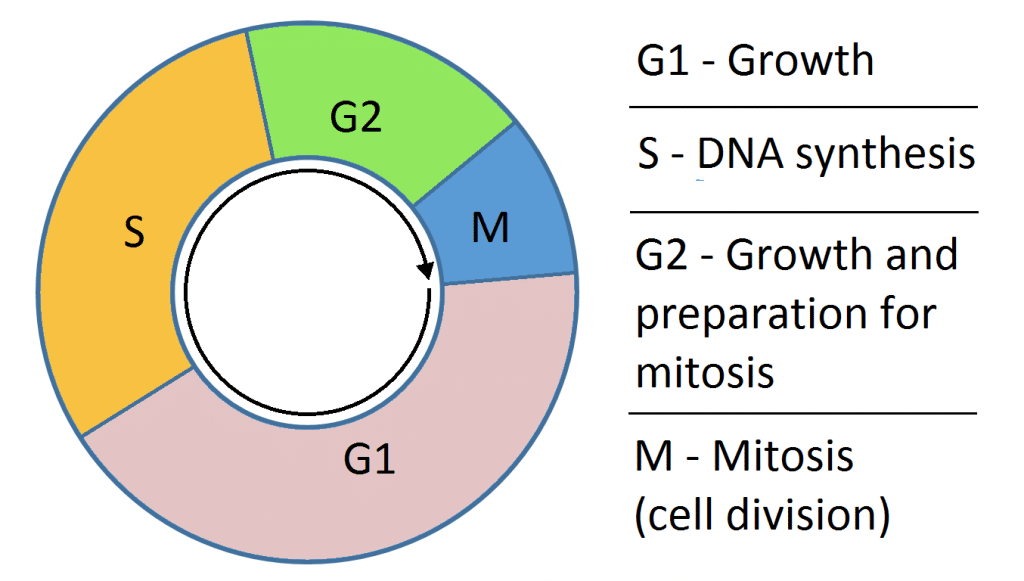
Interphase is divided into G 1 S and G 2 phases. The four stages are competence entry progression and assembly. Mitosis is the process of dividing the duplicated DNA of a cell into two new nuclei.
Overview of the two steps in the photosynthesis process. It occurs in all plants and animals that reproduce by way of gametes or spores. This view is appropriate for all levels of high school biology.
Image from Purves et al Life. The cell cycle can roughly be separated into 2 parts. Because it is a fat only some things that are very tiny like water and oxygen pass through this part.
In plant cells the rigid wall requires that a cell plate be synthesized between the two daughter cells. Although G1 is a phase of the cell cycle it also has four subphases that describe its processes and functions. Meiosis Clearly Explained and Simplified.
As these materials enter the cell in the entry subphase. The Science of Biology. For longer treatments of various aspects of.
This break down also. Meiosis is a type of cell division involved in sexual reproduction. HttpsgooglsugAhv-- Transcription Translatio.
In the process three NAD molecules are reduced to NADH one FAD molecule is reduced to FADH 2 and one ATP or GTP depending on the cell type is produced by substrate-level phosphorylation. Competence refers to the process by which a cell absorbs nutrients and things from outside of the cell membrane. The carbon dioxide then enters the Calvin Cycle with PEP.
The DNA content of a diploid cell in the G1 phase of the cell cycle is measured. Gap phase 1 synthesis phase gap phase 2 and mitosis. In humans the frequency of cell turnover ranges from a few hours in early embryonic development to an average of two to five days for epithelial cells and to an entire human lifetime spent in G 0 by specialized cells such as cortical neurons or cardiac muscle cells.
The rest of the cell cycle interphase accounts for about 90 of the cell cycle. It is made of a double layer of lipids fats imbedded with odd-looking protein molecules. Mitosis animation 480 k OR.
Each step of the cell cycle is. 2 Krebs Cycle 3 The Electron Transport Chain ETC This is a very simple overview of these 3 stages. Sarcomere shortening muscle contraction 1.
In animal cells cytokinesis results when a fiber ring composed of a protein called actin around the center of the cell contracts pinching the cell into two daughter cells each with one nucleus. Glycolysis Stage 1 Glycolysis is the process where 1 glucose molecule in the cells cytoplasm is broken down through several steps into 2 molecules of pyruvate which is then used in the Krebs Cycle stage 2. Depolarisation and calcium ion release.
Organisms that do not depend on oxygen degrade foodstuffs in a process called fermentation. Here the steps involved in the virus life cycle are described with emphasis on entry and exit. After entering the cell and localizing to an intracellular milieu the virus sheds its capsid transcribes its RNA translates its RNA to the viral proteins replicates its genome assembles the viral components and finally exits from the cell.
The length of the cell cycle is highly variable even within the cells of a single organism. Here we look at the stages of mitosis as well as how the cell finally splits to form two new cells. Cellular respiration the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules diverting the chemical energy in these substances into life-sustaining activities and discarding as waste products carbon dioxide and water.
Since 1994 CELLS alive. Mitosis and cytokinesis are the steps during which the cell divides into two daughter cells. If this DNA content is X then the DNA content of the same cell at metaphase of meiosis II.
In eukaryotes the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period called interphase. Through a series of steps citrate is oxidized releasing two carbon dioxide molecules for each acetyl group fed into the cycle. The process of muscular contraction occurs over a number of key steps including.
Figure 1 Representation of the phases of the cell cycle. The main function is to control what goes in and out of the cell. Httpsgoogluf6hh4-- DNA Replication Video.
Actin and myosin cross-bridge formation Sliding mechanism of actin and myosin filaments.


No comments for "Describe the Steps of the Cell Cycle"
Post a Comment